The Art and Science Behind Hair Transplant Procedures
The Art and Science Behind Hair Transplant Procedures
- October 5, 2024
- By Global Hair Centre
- 1545
- Hair Care, Hair Transplant In Dubai
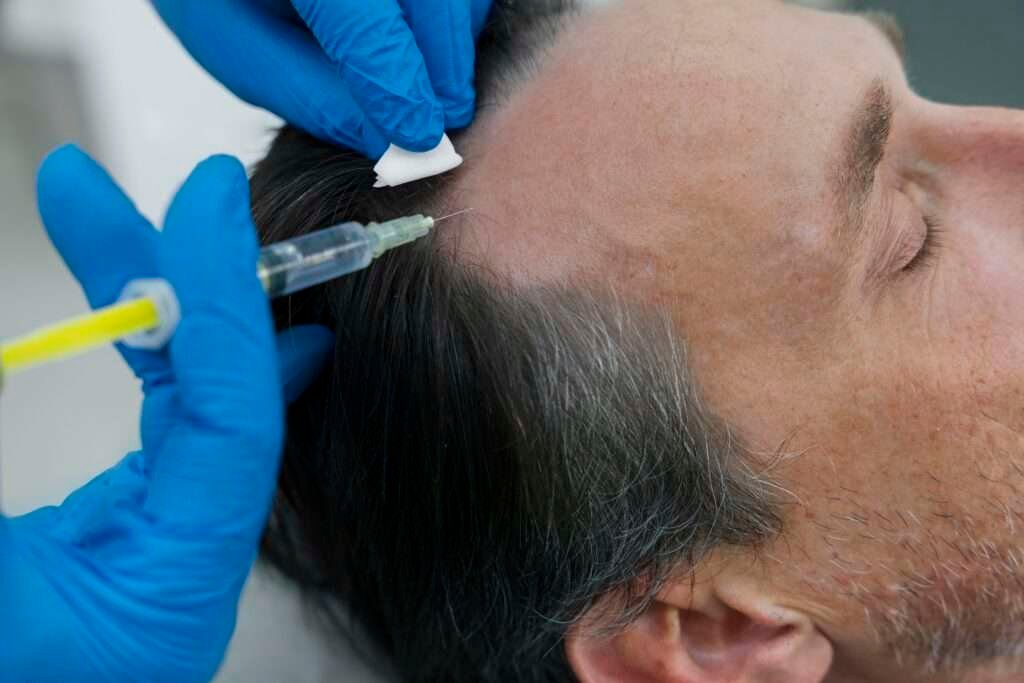
Hair transplant procedures have evolved significantly over the past few decades, combining cutting-edge science with artistic precision to offer transformative solutions for hair loss. Understanding the intricate balance between art and science in hair restoration can shed light on why these procedures are not only effective but also highly personalized. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the scientific principles behind hair transplants, the artistic considerations involved, and how these elements come together to deliver natural-looking results.
The Science of Hair Transplants
Understanding Hair Growth Cycles
To appreciate hair transplant procedures, it’s essential to understand the basic science of hair growth. Hair grows in cycles consisting of three phases:
- Anagen Phase (Growth Phase): This is the active phase of hair growth, lasting 2-6 years, during which hair follicles produce new hair. Approximately 85-90% of the hair on the scalp is in this phase.
- Catagen Phase (Transition Phase): Lasting about 2-3 weeks, this phase marks the end of active growth. The hair follicle shrinks and detaches from the blood supply.
- Telogen Phase (Resting Phase): This phase lasts around 3 months. The hair remains in the follicle but does not grow. Eventually, the hair falls out, making way for new growth.
Understanding these phases is crucial because hair transplant procedures aim to mimic the natural hair growth cycle, ensuring that transplanted hair integrates seamlessly with existing hair.
Hair Follicle Anatomy
Each hair follicle consists of several parts:
- Bulb: The base of the follicle where hair growth begins.
- Papilla: A small, bulb-like structure containing blood vessels that supply nutrients to the hair.
- Matrix: The area where cell division occurs, producing new hair cells.
- Dermal Sheath: Surrounds the hair follicle, supporting and nourishing it.
The success of a hair transplant relies on the ability to harvest and transplant these hair follicles while preserving their complex structure and function.
Techniques in Hair Transplantation
Hair transplant techniques have advanced dramatically, with two primary methods being widely used today:
1. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a minimally invasive technique where individual hair follicles are extracted from the donor area (usually the back of the scalp) and transplanted to the recipient area. The process involves:
- Extraction: Using a small punch tool, individual follicular units are extracted from the donor site.
- Preparation: The harvested follicles are prepared for implantation.
- Implantation: Follicles are inserted into tiny incisions made in the recipient area.
FUE is known for its precision, minimal scarring, and quicker recovery time compared to older methods.
2. Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Also known as strip harvesting, FUT involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area, dissecting it into individual follicular units, and transplanting these units to the recipient area. The process includes:
- Harvesting: A strip of scalp is removed from the donor site.
- Dissection: The strip is divided into individual follicular units.
- Implantation: Follicular units are transplanted to the recipient area.
FUT can provide a larger number of grafts in a single session but may leave a linear scar.
The Role of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy is a non-surgical treatment that complements hair transplant procedures. It involves:
- Extraction: Blood is drawn from the patient.
- Processing: The blood is processed to concentrate platelets and growth factors.
- Injection: The PRP is injected into the scalp to stimulate hair follicles and promote growth.
PRP therapy can enhance the results of hair transplants by improving the health of existing hair follicles and supporting new hair growth.
The Art of Hair Transplants
Designing Natural-Looking Hairlines
The artistic aspect of hair transplants is crucial in achieving a natural-looking result. Key considerations include:
- Hairline Design: A natural hairline follows the unique patterns of individual hair growth and facial features. Surgeons must design hairlines that blend seamlessly with the patient’s natural hair.
- Density and Coverage: Achieving an appropriate density and coverage involves placing hair follicles strategically to avoid a “plucked” appearance. The goal is to create a full, natural-looking head of hair.
- Direction and Angle: Hair follicles must be implanted at the correct angle and direction to mimic natural hair growth. This attention to detail ensures that transplanted hair grows in harmony with existing hair.
Choosing the Right Graft Size
Graft size plays a significant role in the aesthetic outcome of a hair transplant. Different graft sizes can be used:
- Single Follicular Unit Grafts: Ideal for creating a natural hairline and adding detail to the front of the hairline.
- Multi-Follicular Unit Grafts: Used to achieve density in the crown or other areas where more coverage is needed.
The selection of graft size is based on the patient’s hair characteristics and desired outcome.
Customizing Techniques to Individual Needs
Every patient’s hair loss pattern and goals are unique. An artistic approach involves customizing techniques to fit individual needs, such as:
- Assessing Hair Loss Pattern: Understanding the patient’s specific hair loss pattern helps in designing a restoration plan that addresses their unique needs.
- Considering Facial Features: The hairline and overall appearance must complement the patient’s facial features, creating a balanced and harmonious look.
- Incorporating Patient Preferences: The patient’s preferences and expectations are integrated into the treatment plan, ensuring that the final result aligns with their vision.
Combining Art and Science: The Procedure
The successful execution of a hair transplant relies on the seamless integration of both scientific principles and artistic design. Here’s how these elements come together during the procedure:
Pre-Operative Planning
Before the procedure, thorough planning is essential. This includes:
- Consultation: Discussing goals, assessing hair loss, and selecting the appropriate technique.
- Designing the Hairline: Creating a detailed plan for the hairline and graft placement.
- Preparing the Scalp: Ensuring the donor and recipient areas are prepped for the procedure.
Performing the Procedure
During the procedure, the scientific and artistic aspects are put into practice:
- Harvesting Grafts: Precision is key in extracting and preparing grafts, ensuring that hair follicles are handled carefully to maintain their integrity.
- Implanting Grafts: Artistic skill is applied in placing grafts to achieve a natural look, paying attention to direction, angle, and density.
Post-Operative Care
Post-operative care is crucial for optimal results:
- Follow-Up: Regular check-ups to monitor healing and hair growth.
- Care Instructions: Guidelines on scalp care, medication, and activity restrictions to support recovery.
Success Stories and Outcomes
The combination of art and science in hair transplants has led to numerous success stories. Patients who have undergone hair transplant procedures often report:
- Enhanced Self-Esteem: The restoration of a full head of hair boosts confidence and improves self-image.
- Natural-Looking Results: Carefully designed hairlines and well-executed procedures result in natural-looking hair.
- Long-Term Satisfaction: Patients enjoy long-term results and a renewed sense of normalcy.
Future Trends in Hair Transplantation
The field of hair transplantation continues to evolve, with promising trends on the horizon:
1. Advanced Technologies
Emerging technologies, such as robotic-assisted FUE and improved PRP techniques, promise even greater precision and efficiency in hair transplants.
2. Genetic and Stem Cell Research
Research into genetics and stem cells may lead to breakthroughs in treating hair loss, offering new options for restoration and prevention.
3. Personalized Treatments
Future advancements may allow for more personalized treatment plans, tailored to individual genetic profiles and hair growth patterns.
The Role of Donor Area Evaluation
A critical component of the hair transplant process is evaluating the donor area—the part of the scalp from which hair follicles are harvested. The quality and quantity of hair in this area can significantly impact the outcome of the transplant. Key factors to consider include:
- Hair Density: Higher density in the donor area provides more follicles for extraction, which can improve the results of the transplant.
- Hair Quality: Strong, healthy hair follicles yield better results than weaker or miniaturized follicles.
- Scalp Condition: A healthy scalp with good blood circulation supports effective follicle extraction and healing.
Global Hair Dubai and other leading clinics use advanced diagnostic tools to assess the donor area thoroughly, ensuring optimal follicle extraction and utilization.
2. Post-Transplant Hair Growth Phases
Understanding the phases of hair growth post-transplant is essential for setting realistic expectations. After a transplant, hair goes through several stages:
- Shedding Phase: Often, transplanted hair sheds within the first few weeks as part of the normal cycle. This can be distressing but is a typical part of the process.
- Regrowth Phase: New hair growth typically begins around 3-6 months post-surgery. The hair may initially be fine and thin but gradually thickens over time.
- Maturation Phase: Full results are usually visible 12-18 months after the procedure, with hair achieving its final thickness and density.
Understanding these phases helps patients manage their expectations and appreciate the gradual nature of hair restoration.
3. Combining Hair Transplants with Other Treatments
Many patients choose to combine hair transplant procedures with other treatments to enhance results. Common complementary treatments include:
- Topical Medications: Products like minoxidil can support and enhance the results of hair transplants by stimulating existing follicles.
- Oral Medications: Finasteride, a medication that blocks DHT, can slow hair loss and improve the effectiveness of hair transplants.
- Laser Therapy: Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) can increase blood flow and promote hair growth, providing additional support post-transplant.
Integrating these treatments can address different aspects of hair loss and contribute to a more comprehensive approach to restoration.
4. Psychological Aspects of Hair Restoration
The psychological impact of hair loss and subsequent restoration is significant. Hair loss can affect self-esteem and emotional well-being, while hair restoration can lead to substantial psychological benefits:
- Increased Confidence: Successfully restoring hair can significantly boost self-esteem and confidence.
- Emotional Well-being: The psychological relief from addressing hair loss can lead to improved overall mental health and quality of life.
Understanding these psychological aspects helps clinics provide a more holistic approach to treatment, addressing both physical and emotional needs.
5. Ethical Considerations in Hair Transplantation
Ethical considerations play an important role in the field of hair transplantation:
- Informed Consent: Patients must be fully informed about the risks, benefits, and limitations of the procedure. Ensuring that patients understand and consent to the treatment plan is crucial.
- Realistic Expectations: Clinics must set realistic expectations for patients, avoiding over-promising results that may not be achievable.
- Transparency: Ethical practices include transparent communication about costs, potential complications, and post-procedure care.
Adhering to these ethical standards ensures that patients receive responsible and professional care throughout their hair restoration journey.
6. The Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements continue to shape the field of hair transplantation, offering new possibilities and improvements:
- Robotic-Assisted Techniques: Advanced robotic systems assist in precise follicle extraction and implantation, improving accuracy and consistency.
- AI and Machine Learning: Emerging technologies use artificial intelligence to analyze hair loss patterns and predict outcomes, leading to more personalized treatment plans.
- Regenerative Medicine: Research into stem cell therapy and regenerative medicine holds promise for future breakthroughs in hair restoration.
Conclusion
The art and science behind hair transplant procedures represent a harmonious blend of technical expertise and creative design. Understanding the scientific principles of hair growth and follicle anatomy provides the foundation for effective hair restoration, while the artistic elements ensure natural-looking, aesthetically pleasing results. As technology and techniques continue to advance, the future of hair transplantation promises even more innovative and personalized solutions, further enhancing the transformative impact of these procedures. Whether you’re considering a hair transplant or simply interested in the field, appreciating the intricate balance of art and science can offer a deeper understanding of how these remarkable transformations are achieved.
Related Blogs

- August 20, 2025
Hair Transplant in Dubai: Your Ultimate.
Hair loss can significantly affect self-confidence. However, with modern hair transplant techniques in Dubai, restoring your natural hairline has never.
Read More
- August 2, 2025
Hair Transplant in Dubai: The Ultimate.
Introduction: A New Era for Hair Transplant in Dubai Hair loss can be devastating, especially for men in their 20s,.
Read More
